pKa Prediction
Knowing the pKa of a molecule is key to understanding its structure and reactivity. Rowan's pKa prediction workflow uses machine-learned interatomic potentials and semiempirical solvation energies to enable fast and accurate prediction of pKa values with minimal empiricism.
How It Works
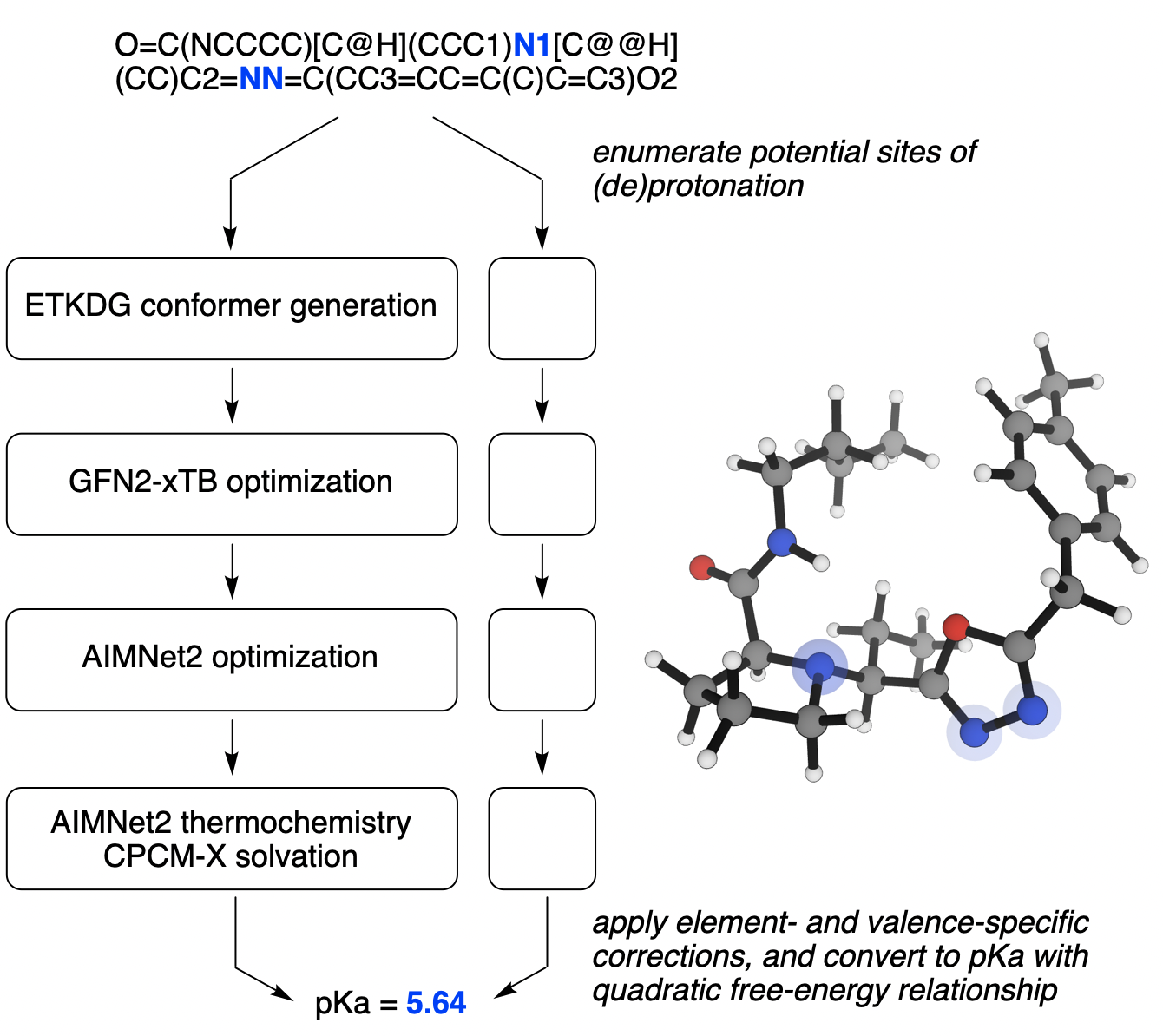
An overview of how Rowan predicts pKa values.
At a high level, the Rowan pKa prediction workflow works much like other quantum chemistry–based pKa prediction workflows, but replaces the slow DFT calculations in these workflows with neural network potentials, leading to multiple orders-of-magnitude speedup. More specifically, single-point energies and geometry optimizations are computed using the AIMNet2 model trained on ωB97M-D3BJ/def2-TZVPP training data, henceforth abbreviated as AIMNet2. Since AIMNet2 does not take solvation into account, ∆Gsolv is computed from a single-point GFN2-xTB calculation with the CPCM-X implicit water model.
The workflow begins by iteratively adding or removing hydrogens to the molecule of interest using RDKit and quickly estimating the proton affinity for the conjugate acid/conjugate base pair using AIMNet2 single-point energy calculations. If (de)protonation is predicted to yield a pKa value close to the desired range, conformers are generated using the ETKDG algorithm and optimized using the MMFF94 forcefield. After removing redundant geometries, low-energy conformers are then optimized using GFN2-xTB, single-point energies are calculated using AIMNet2, and the lowest-energy conformers undergo full optimization with AIMNet2 to generate a final energy for each conformer, including a CPCM-X solvent correction.
Following Pracht and Grimme, we combine energies from each conformer via Boltzmann averaging to generate a single hybrid ∆G for the conjugate acid/conjugate base pair and apply a quadratic free-energy relationship to convert this into pKa values. To correct for systematic errors in thermochemistry and solvation, we also add an element- and valence-specific constant to ∆G for each conjugate acid/conjugate base pair. (The correction for divalent oxygen, i.e. deprotonation of ROH, is defined as zero to eliminate extra degrees of freedom.) The final workflow contains 7 empirical parameters, shown here:
| Coefficients for Free-Energy Relationship | |
|---|---|
| C0 | –123.243 |
| C1 | 0.507 mol/kcal |
| C2 | –1.740e-4 mol2/kcal2 |
| Element-/Valence-Specific Constants | (kcal/mol) |
| N3 | 3.914 |
| N4 | 5.131 |
| C4 | 6.039 |
| O2 | 0.00 (defined) |
| S2 | –5.144 |
Accuracy
On a variety of benchmarks (also described in the preprint), Rowan pKa displays mean absolute errors of around 1 pKa unit, and decent predictive accuracy as assessed by Kendall's τ and r2 values. Here's the performance on the SAMPL7 benchmark set:
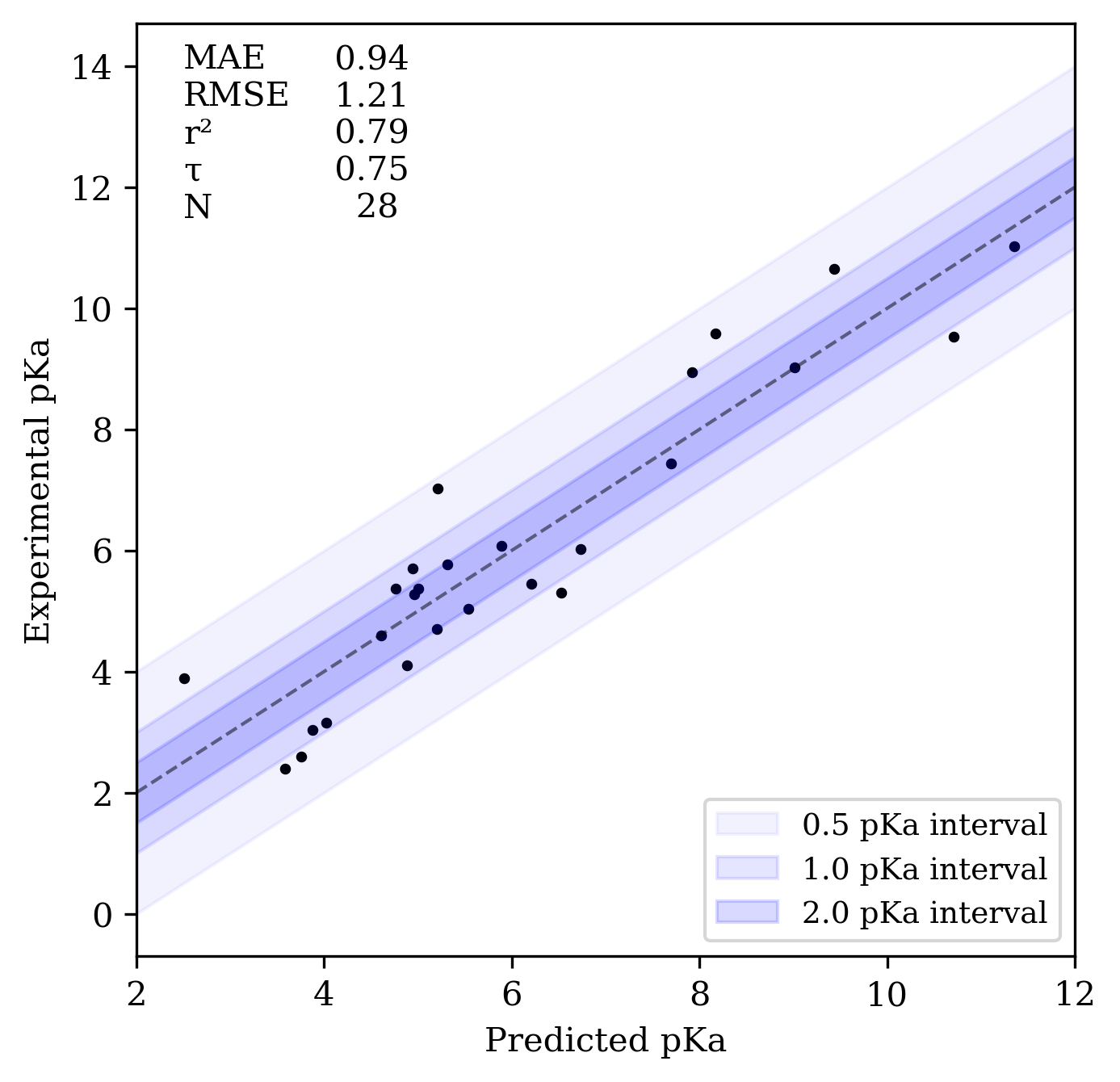
Rowan pKa prediction workflow's performance on SAMPL7
For a full list of all assays surveyed, see the preprint.
Modes
Rowan pKa can be run in three modes: careful, rapid, or reckless. Here's what selecting each mode tunes:
| Mode | Careful | Rapid | Reckless |
|---|---|---|---|
| buffer around desired range (pKa units) | 10 | 5 | 5 |
| number of initial conformations | 250 | 100 | 50 |
| initial energy cutoff (kcal/mol) | 15 | 10 | 5 |
| RMSD similarity cutoff (Å) | 0.10 | 0.25 | 0.50 |
| max number of conformers (xTB) | 20 | 10 | 3 |
| final energy cutoff (kcal/mol) | 5 | 5 | 3 |
| max number of conformers (AIMNet2) | 10 | 3 | 1 |
In general, we've found that the "careful" mode offers the best combination of speed and accuracy, but faster modes offer increased performance where high throughput is required.